Optimizing gas costs has become a defining challenge for developers building on modular MEV auction platforms. As Ethereum trades at $4,466.17 today, the pressure to maximize every wei spent is more intense than ever. With multidimensional gas pricing concepts gaining traction and dynamic fee environments shaping the way auctions operate, effective strategies are no longer optional-they’re essential for sustainable returns and competitive edge.
Leveraging Multidimensional Gas Pricing for Transaction Optimization
The introduction of multidimensional gas pricing, pioneered by Vitalik Buterin, is transforming how developers approach transaction cost optimization. Instead of treating gas as a single scalar value, this paradigm breaks costs into several dimensions (such as computation, storage, and bandwidth), allowing for far more precise fee allocation per transaction type. For modular MEV auction builders, this means:
- Optimizing smart contract logic to minimize the most expensive resource dimension
- Designing transactions that exploit underutilized capacity in the network’s multidimensional fee structure
- Making real-time decisions on transaction routing based on which gas vector is least congested at any moment
The result? More granular control over costs and better alignment with market realities. As multidimensional fee markets mature, expect smart contracts that dynamically adapt their behavior based on real-time pricing signals across all vectors-not just base gas price.
Implementing Dynamic Fee Bidding Based on Real-Time Auction Data
Static gas bidding is a relic of the past in today’s auction-driven blockspace economy. Developers now have access to sophisticated analytics that surface live auction data, revealing current blockspace demand and competitive bid levels. By implementing dynamic fee bidding algorithms, builders can:
- Avoid overpaying during low-traffic periods by monitoring mempool congestion in real time
- Increase bid precision during high-value MEV opportunities when seconds (and gwei) matter most
- Integrate feedback loops from recent auction outcomes to continually refine their bidding logic
This adaptive approach not only minimizes unnecessary expenditure but also improves the probability of successful inclusion during volatile market events.
Top 5 Strategies to Optimize Gas in Modular MEV Auctions
-

Leverage Multidimensional Gas Pricing for Transaction OptimizationUtilize Multidimensional Gas Pricing (as introduced by Vitalik Buterin) to fine-tune transaction costs by accounting for various resource constraints, such as computation, storage, and calldata. This approach enables developers to optimize each transaction’s resource usage, reducing overall gas expenditure in modular MEV auction environments.
-
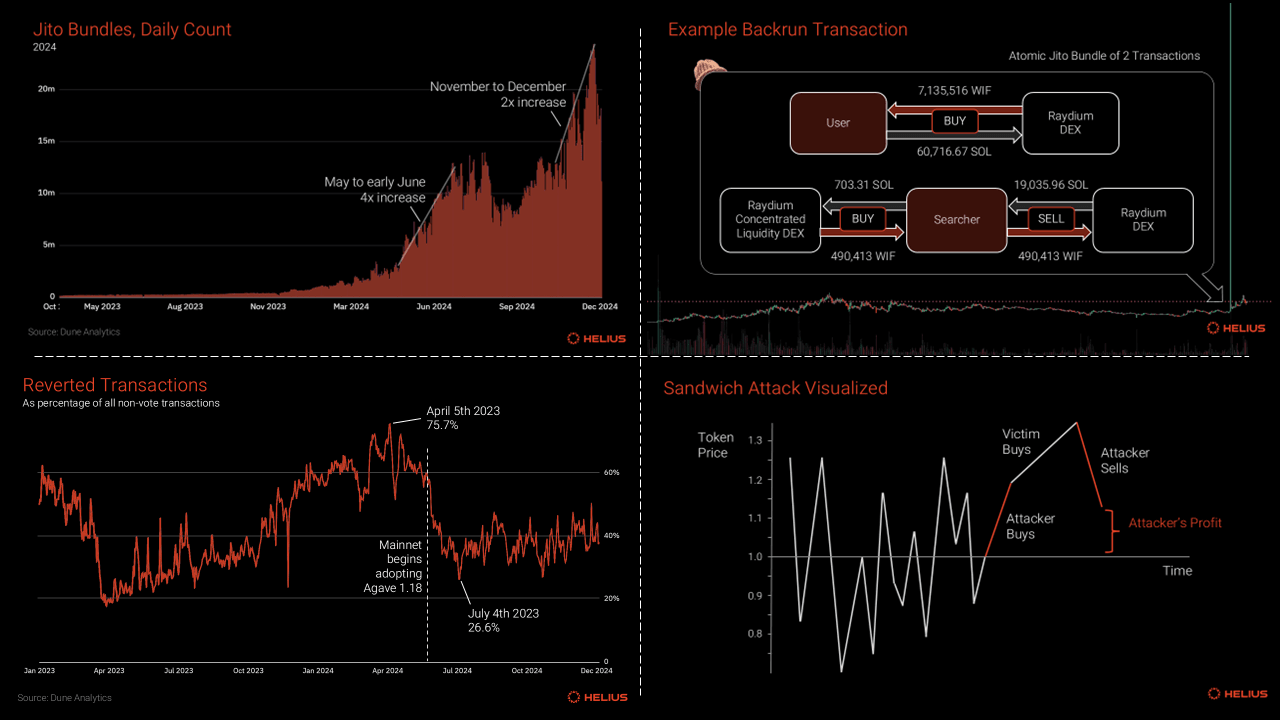
Implement Dynamic Fee Bidding Based on Real-Time Auction DataAdopt dynamic fee mechanisms that adjust gas bids in response to real-time auction congestion and network conditions. Tools like MEV-Boost enable more precise fee bidding, ensuring developers avoid overpaying while maintaining transaction priority.
-

Utilize Batch Transaction Bundling to Reduce Redundant Gas ExpenditureBundle multiple related transactions into a single batch using platforms such as Flashbots or Blocknative. This reduces per-transaction overhead and minimizes redundant gas costs, especially in high-frequency MEV auction scenarios.
-

Integrate Gas Option Derivatives for Predictable Fee ManagementLeverage emerging financial instruments like gas options derivatives (as discussed in recent research) to hedge against volatile gas prices. These tools empower developers to lock in predictable transaction fees, enhancing cost control and operational certainty.
-
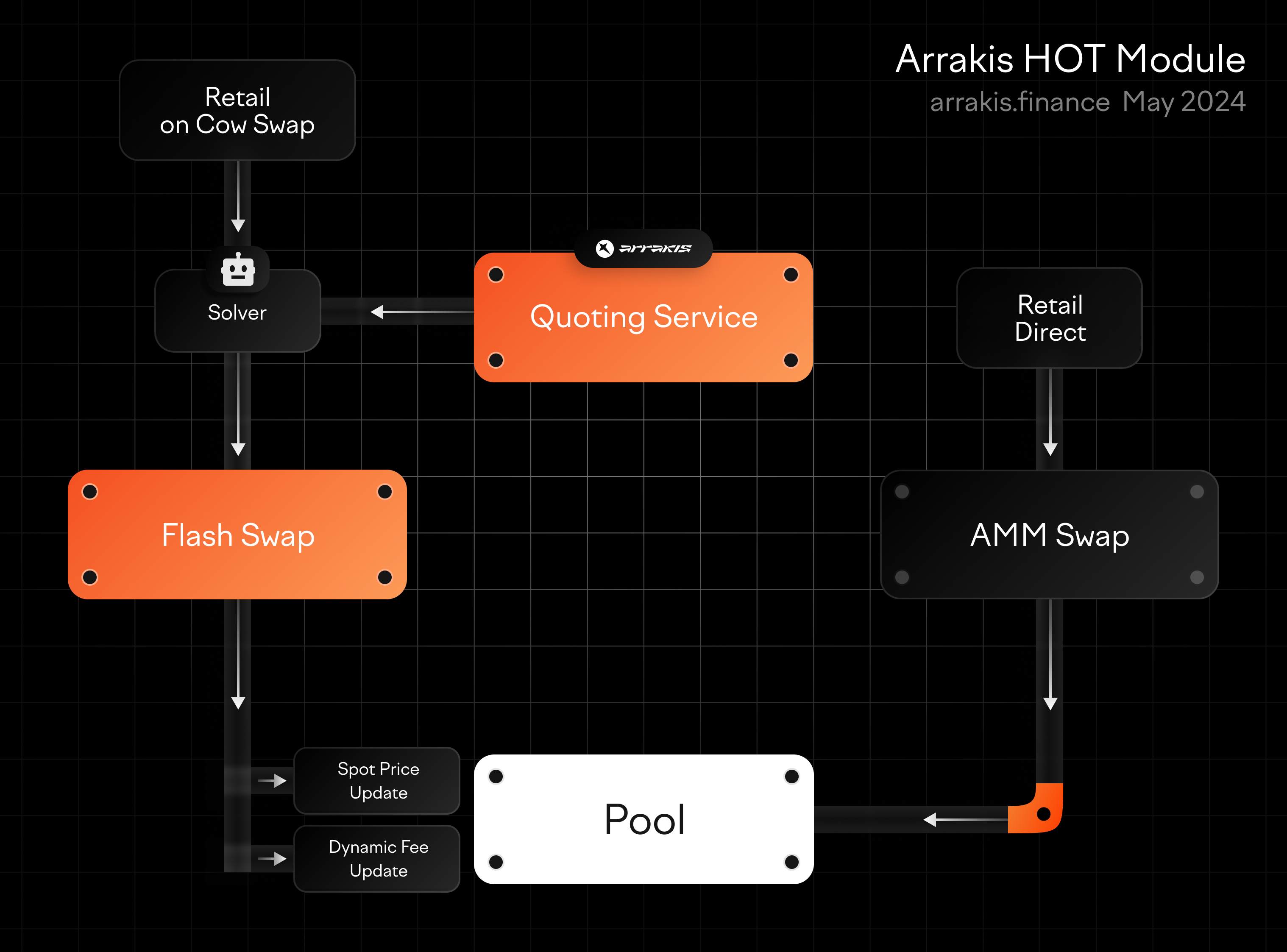
Adopt MEV-Aware Routing to Minimize Unnecessary Gas ConsumptionImplement MEV-aware routing solutions, such as Manifold Finance or Arrakis Finance, to direct transactions through the most gas-efficient paths. This approach avoids unnecessary computation and reduces wasted gas in modular auction workflows.
Utilizing Batch Transaction Bundling to Reduce Redundant Gas Expenditure
Batched transaction bundling-the practice of aggregating multiple operations into a single submission-has proven especially valuable in modular MEV environments. By consolidating related actions (such as swaps, arbitrages, or liquidations) within one atomic bundle, developers can:
- Dramatically reduce per-operation overhead by sharing fixed costs across multiple intents
- Simplify settlement flows and minimize redundant state updates or external calls
- Enhance composability within modular protocols by enabling cross-contract actions without repeated execution penalties
This technique aligns directly with research showing batch processing’s effectiveness in lowering aggregate fees (source). For developers orchestrating complex MEV strategies or large-scale order flow auctions, batch bundling isn’t just efficient-it’s foundational.
The Next Layer: Integrating Gas Option Derivatives and MEV-Aware Routing
The evolution doesn’t stop at batching or dynamic fees. Forward-thinking teams are exploring derivatives markets for gas options and routing algorithms that actively minimize unnecessary consumption-both topics we’ll explore next.
Gas cost volatility is a persistent challenge, especially as Ethereum’s price remains at $4,466.17. Developers seeking predictability and risk management are increasingly turning to gas option derivatives. These financial instruments allow teams to hedge against sudden spikes in transaction fees by locking in future gas prices or purchasing options that pay out when costs exceed a certain threshold.
- Predictable Budgeting: By integrating gas option derivatives, projects can forecast their operational expenses with greater accuracy, crucial for protocols executing time-sensitive MEV strategies.
- Risk Mitigation: Option contracts function much like insurance, providing a buffer during periods of mempool congestion or market-driven fee surges.
- Strategic Flexibility: Developers can dynamically allocate resources between direct bidding and hedged positions based on real-time auction analytics and fee projections.
This approach is supported by recent research into EIP-1559-like fee models and option pricing methodologies (source). As these derivatives mature, expect wider adoption among modular MEV auction platforms aiming for sustainable, cost-efficient growth.
Adopting MEV-Aware Routing to Minimize Unnecessary Gas Consumption
The final frontier in gas optimization is MEV-aware routing: the practice of algorithmically directing transactions through the most efficient pathways across blockspace markets. Instead of blindly submitting orders into congested mempools or high-fee blocks, advanced routers analyze both historical and real-time data to identify routes that minimize slippage and redundant gas expenditure.
- Cross-Chain and Cross-Rollup Intelligence: Modern routers can split order flow between L1 and L2 networks, or even across different chains, optimizing for lowest total execution cost.
- Avoiding Hotspots: By steering clear of blocks targeted by aggressive searchers or known arbitrageurs, developers reduce the likelihood of costly failed transactions or unnecessary bid escalation.
- Sustainable Network Participation: MEV-aware routing encourages fairer resource allocation and reduces the systemic risks caused by inefficient transaction flooding.
This strategy echoes the latest thinking from platforms like Manifold Finance and aligns with the growing trend toward modular protocol composability (source). For developers focused on optimizing gas costs while maintaining robust participation in MEV auctions, intelligent routing is quickly becoming non-negotiable.

Strategic Takeaways for Modular MEV Auction Developers
The landscape of modular MEV auction development is evolving rapidly. As multidimensional pricing structures become standard and new tools emerge for dynamic fee management, developers must rethink their approach to blockchain gas optimization. The five actionable strategies discussed provides leveraging multidimensional pricing, implementing dynamic bidding, utilizing batch bundling, integrating gas options, and adopting MEV-aware routing: are not only best practices but essential pillars for any team seeking efficiency and long-term sustainability in DeFi’s competitive environment.
The next wave of innovation will likely be driven by those who combine these strategies into adaptive frameworks that respond fluidly to changing market conditions. With Ethereum holding steady at $4,466.17, every basis point saved on transaction fees compounds over time, directly impacting protocol profitability and user experience alike.
Checklist: Gas Optimization Strategies for Modular MEV Auctions
-

Leverage Multidimensional Gas Pricing for Transaction Optimization: Utilize Vitalik Buterin’s multidimensional gas pricing framework to optimize transactions by accounting for multiple resource constraints (e.g., computation, storage, calldata). This approach enables more granular fee assessments and can lead to significant gas savings in modular MEV auction environments.
-

Implement Dynamic Fee Bidding Based on Real-Time Auction Data: Use live auction analytics and network congestion metrics to dynamically adjust gas bids. Platforms like MEV-Boost and Blocknative Gas Estimator provide actionable data to help avoid overpaying for transaction inclusion, ensuring competitive yet efficient fee strategies.
-

Utilize Batch Transaction Bundling to Reduce Redundant Gas Expenditure: Combine multiple operations into a single transaction using batch processing tools such as Flashbots or Manifold Finance. This reduces per-transaction overhead and minimizes total gas spent in modular MEV auction workflows.
-
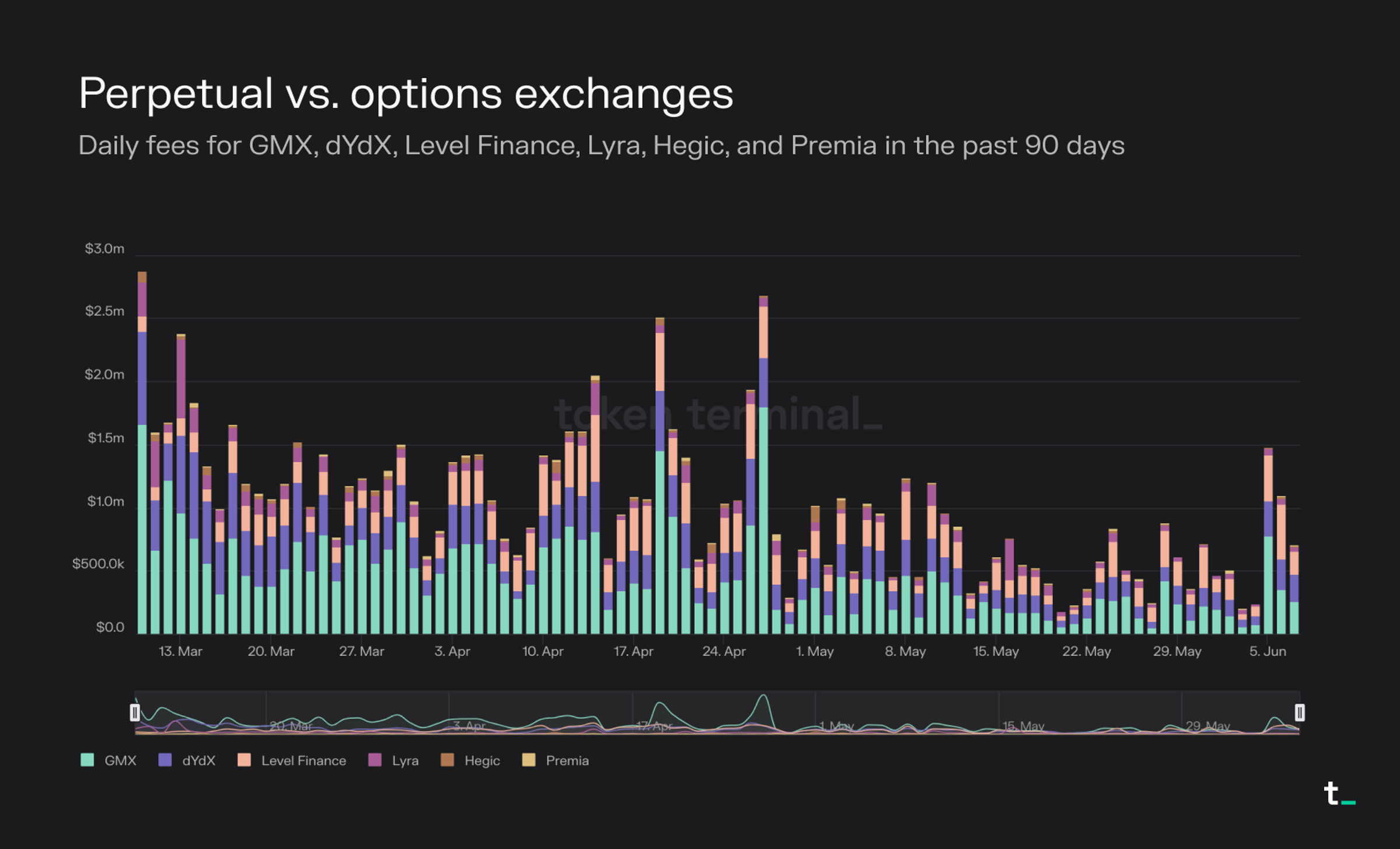
Integrate Gas Option Derivatives for Predictable Fee Management: Explore platforms like ChainGas or research from ScienceDirect on gas options to hedge against volatile transaction fees. Gas derivatives enable developers to lock in predictable costs, improving budgeting and financial planning for MEV auction participation.
-

Adopt MEV-Aware Routing to Minimize Unnecessary Gas Consumption: Integrate MEV-aware routing solutions, such as Arrakis Finance or Blocknative, to intelligently direct transactions and avoid routes prone to excessive MEV extraction and gas waste.






