Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) has long been a contentious issue in decentralized finance. It represents the profit that can be captured by reordering, including, or excluding transactions within a block. While MEV extraction has driven innovation in blockchain transaction ordering, it has also led to network congestion, higher execution costs, and centralization risks. The arrival of sealed-bid MEV auctions is now transforming this landscape, offering a more equitable and efficient approach for both traders and protocol participants.

What Are Sealed-Bid Auctions and Why Do They Matter?
In traditional MEV extraction, searchers often flood the network with multiple competing transactions, each vying for inclusion in the next block. This “gas war” not only increases costs for everyone but also undermines fairness by favoring those with deeper pockets or faster infrastructure. A sealed-bid auction flips this model on its head: each participant submits one confidential bid without knowing what others are offering. The highest bidder wins and pays their bid amount (in first-price models), or the second-highest price (in second-price models).
This seemingly simple shift brings powerful benefits:
Key Advantages of Sealed-Bid Auctions in DeFi
-
Reduced Network Congestion: Sealed-bid auctions limit each searcher to a single confidential bid, significantly decreasing transaction spam and making blockchain networks like Ethereum more efficient.
-

Fairer Value Distribution: By enabling equitable sharing of MEV profits among validators, stakers, and the wider community—as seen in HyperFlash’s MEV Auction Mechanism—sealed-bid auctions help reduce centralization risks.
-
Enhanced Transparency and Trust: The confidential nature of sealed-bid auctions minimizes opportunities for collusion and manipulation, fostering a more transparent and trustworthy DeFi environment.
-

Mitigation of Gas Fee Bidding Wars: Platforms like Arbitrum’s TimeBoost use sealed-bid auctions to allocate priority access, reducing competitive gas fee escalation and redistributing MEV profits—such as the $30 million annual revenue contributed to the ARB DAO treasury.
-
Support for Advanced Applications: Sealed-bid auction systems, such as Manifold Finance’s MEV Protocol, allow for features like multiple winners per slot and multi-slot bidding, enabling more sophisticated and flexible transaction ordering strategies.
The move toward sealed-bid mechanisms is already reshaping how orderflow marketplaces operate, encouraging rational bidding close to true MEV value, reducing spam, and fostering healthier competition among searchers.
Real-World Implementations: HyperFlash, Arbitrum TimeBoost and Manifold Finance
The DeFi ecosystem is now witnessing live deployments of these auction formats:
- HyperFlash’s Staking Protocol: By integrating sealed-bid first-price auctions for transaction inclusion rights, HyperFlash enables MEV searchers to compete fairly while distributing profits more evenly across validators and stakers.
- Arbitrum’s TimeBoost: This innovative system allocates a 200-millisecond fast lane every minute through a sealed-bid second-price auction. Searchers compete for priority access; notably, 97% of TimeBoost revenue goes directly to the ARB DAO treasury, estimated at $30 million annually.
- Manifold Finance’s Multi-Winner Protocol: Unlike single-winner models, Manifold allows multiple winners per slot. This supports advanced use cases such as multi-slot bidding and priority-sensitive applications on Ethereum.
The Broader Impact: Fairness, Efficiency and Decentralization
The adoption of sealed-bid auction mechanisms brings several systemic advantages to blockchain networks:
- Reduced Network Congestion: Limiting bids per participant curbs transaction spam and stabilizes execution costs.
- Fairer Value Distribution: Proceeds from MEV are more equitably shared among stakeholders rather than concentrated among well-capitalized searchers or validators.
- Transparency and Trust: Sealed bids diminish collusion risks and manipulation opportunities that plagued open mempool-based strategies.
This evolution is especially important as orderflow marketplace solutions mature, enabling users to optimize their MEV strategies while supporting network health. For those seeking deeper technical dives or practical guides on implementing these systems, explore our comprehensive resources at Modular Mev Auctions.
As the sealed-bid model gains traction, it is also catalyzing a shift in how DeFi protocols and their communities approach MEV strategy optimization. Rather than relying on brute-force gas bidding or opaque off-chain deals, these auctions offer a structured, transparent framework for value extraction that aligns incentives across all participants. This is especially relevant as more sophisticated blockspace market solutions emerge, demanding both efficiency and fairness in transaction ordering.
Protocols like HyperFlash and Arbitrum have set new benchmarks for revenue sharing and community alignment. By funneling proceeds from sealed-bid auctions, such as Arbitrum’s $30 million annual TimeBoost revenue, directly into DAOs or validator pools, these systems not only reward infrastructure providers but also reinforce the decentralized ethos of blockchain networks. This redistribution of MEV profits is a marked departure from earlier eras where only a handful of well-resourced actors benefited disproportionately.
Challenges Ahead and What’s Next for Sealed-Bid Auctions
Despite their advantages, sealed-bid MEV auctions are not without challenges. Protocol designers must carefully calibrate auction parameters to prevent new forms of manipulation or collusion. There are open questions around optimal slot durations, bid confidentiality guarantees, and how to handle edge cases such as failed bids or validator misbehavior. Ensuring robust monitoring and analytics will be crucial as these systems scale.
Moreover, user education remains vital. As more traders and developers interact with orderflow marketplace solutions, understanding the nuances of sealed-bid formats, and their implications for execution quality, will become an essential skillset. Platforms that offer real-time analytics, transparent auction data, and actionable insights can help bridge this knowledge gap.
The rise of sealed-bid MEV auctions marks a turning point for decentralized finance. By prioritizing fairness, reducing network congestion, and enabling equitable value distribution, these mechanisms are setting new standards for blockchain transaction ordering. As adoption widens across major protocols and Layer 2s, expect continued innovation in auction design, and a more level playing field for all participants in the rapidly evolving DeFi landscape.
Five Ways Sealed-Bid MEV Auctions Are Shaping Orderflow Marketplaces
-

1. Reducing Network Congestion and Spam: Sealed-bid auctions require searchers to submit a single confidential bid rather than flooding the network with multiple transactions, significantly reducing transaction spam and improving overall network efficiency.
-

2. Enabling Fairer MEV Value Distribution: By allocating MEV profits more equitably among validators, stakers, and the broader community, sealed-bid auctions mitigate centralization risks and promote a healthier DeFi ecosystem. For example, Arbitrum’s TimeBoost redistributes 97% of auction revenue to the ARB DAO treasury.
-

3. Enhancing Transparency and Trust: The confidential nature of sealed-bid auctions minimizes collusion and manipulation, fostering greater transparency and trust in orderflow marketplaces.
-

4. Supporting Advanced Auction Models: Platforms like Manifold Finance have introduced MEV protocols with multi-winner sealed-bid auctions, enabling priority-sensitive transactions and multi-slot bidding for more sophisticated value capture and distribution.
-
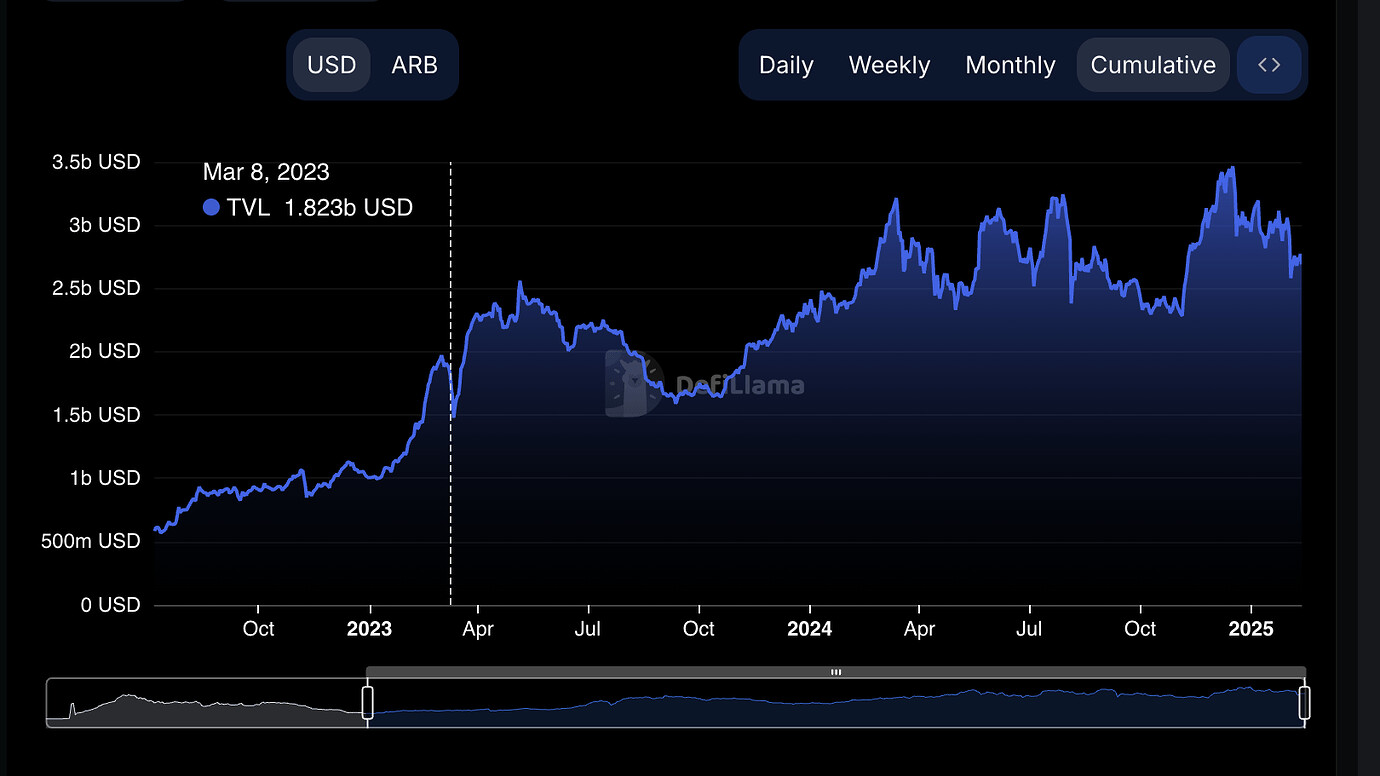
5. Lowering Execution Costs for Users: By curbing gas fee bidding wars and promoting rational, competitive bidding, sealed-bid auctions help achieve best execution for users, reducing the overall cost of transaction inclusion. Arbitrum’s TimeBoost is a leading example of this benefit in action.






