The decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape is undergoing a profound transformation as hybrid settlement models gain traction among both protocol designers and advanced traders. These approaches, which blend the speed of off-chain sequencing with the trustless security of on-chain settlement, are rapidly redefining how transactions are executed and finalized in DeFi ecosystems. As the race for faster, fairer, and more modular infrastructure intensifies, understanding the interplay between sequencers and modular auctions becomes essential for anyone seeking to optimize transaction throughput or extract maximal value from blockspace.

Sequencers: The Backbone of Hybrid Settlement DeFi
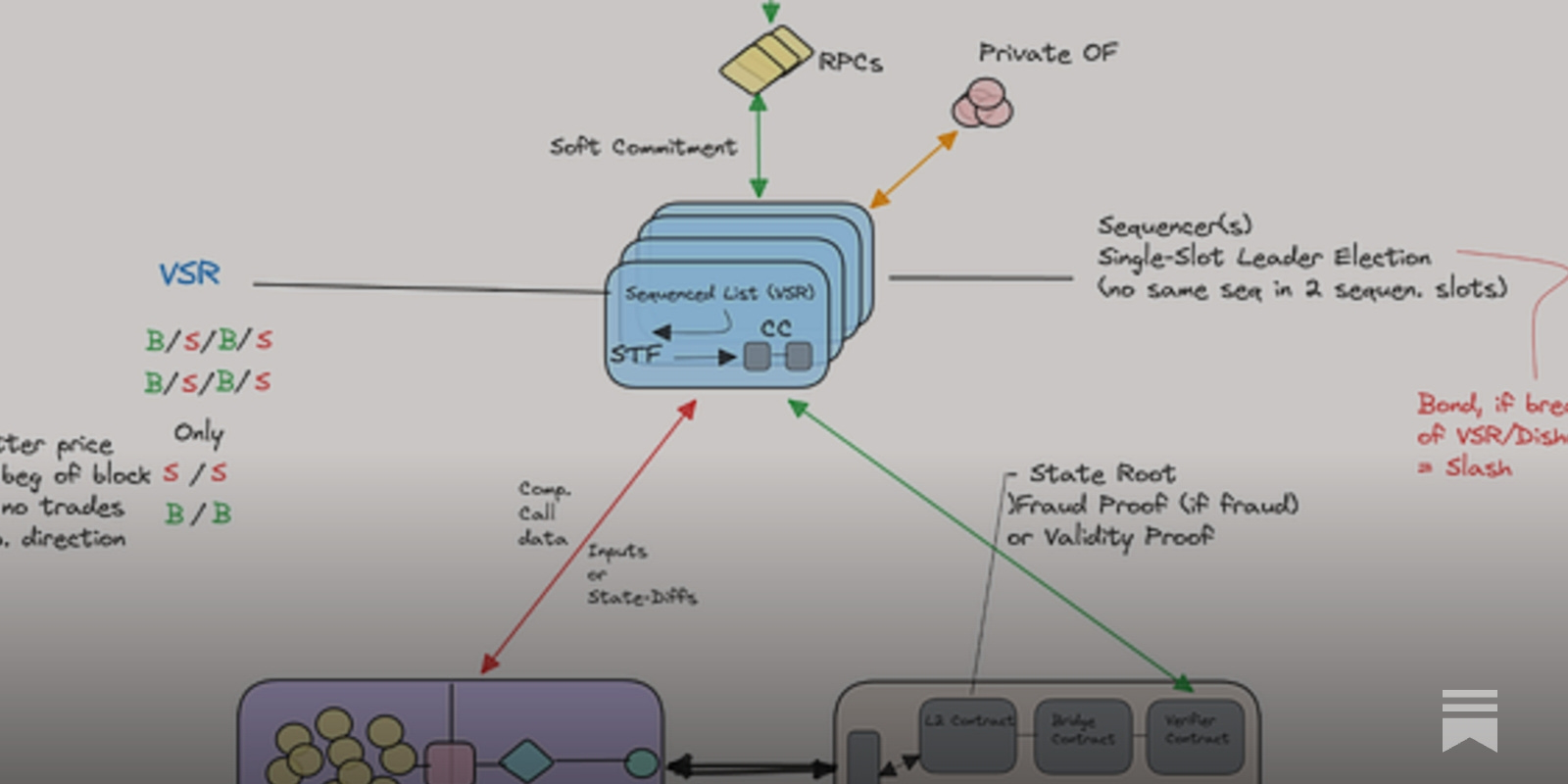
At the heart of many next-generation DeFi protocols are sequencers – entities (or sometimes networks) responsible for ordering transactions before they are committed to a blockchain. In hybrid models, sequencers operate off-chain to enable near-instant transaction ordering, while final settlement occurs on-chain for transparency and security. This duality is exemplified by platforms like Vertex Protocol, where an off-chain sequencer delivers exchange-level speed without compromising asset custody or decentralization. By separating order matching from settlement, these systems can achieve latencies that rival centralized exchanges – a dramatic leap forward for DeFi transaction speed.
The evolution does not stop at generic sequencing. Recent innovations such as Application-Specific Sequencers (ASS) are allowing developers to tailor sequencing logic to the unique needs of their dApps. This approach unlocks new possibilities for custom MEV management strategies and granular control over transaction ordering rules – critical for applications with specialized requirements or regulatory considerations.
Modular Auctions: Customizing Data Availability and Settlement
Alongside advances in sequencing, modular auctions have emerged as a powerful tool for optimizing blockspace allocation and ensuring fair access to high-value transaction inclusion opportunities. Unlike monolithic auction designs that tie together all components of execution, data availability (DA), and settlement into a single protocol stack, modular auctions let builders mix-and-match components based on performance needs or compliance mandates.
Cero Network’s multi-DA, multi-settlement sequencer is a standout example of this trend. By enabling rollups to select between shared or dedicated sequencing options, choose from multiple DA layers (public or private), and opt into various settlement schemes, Cero provides unprecedented flexibility at every step of the transaction lifecycle (source). This level of customization empowers projects ranging from high-frequency trading venues to privacy-focused applications with tools to fine-tune throughput, censorship resistance, and user experience.
Key Benefits of Hybrid Settlement Models in DeFi
-

Enhanced Scalability and Efficiency: By integrating off-chain sequencers with on-chain settlement, hybrid models like Vertex Protocol achieve rapid transaction processing speeds comparable to centralized exchanges, while maintaining the security and transparency of blockchain-based settlement.
-

Greater Flexibility Through Modularity: Solutions such as Cero’s multi-DA, multi-settlement sequencer empower DeFi platforms to select from multiple data availability and settlement layers, allowing for tailored configurations that suit diverse application needs.
-
Improved Fairness in Transaction Ordering: Models like Flashbots’ FBA-FCFS combine auction-based bidding with first-come, first-served processing, helping to mitigate Miner Extractable Value (MEV) issues and promote equitable transaction inclusion.
-

Increased Security and Decentralization: Hybrid models maintain asset custody and final settlement on-chain, reducing the risks associated with centralized control and ensuring that user funds remain secure and transparent.
-

Customizable User Experience: The modular approach allows DeFi platforms to optimize for specific use cases, such as high-frequency trading or regulated asset settlement, enhancing performance and user satisfaction across different market segments.
Flashbots FBA-FCFS: Balancing Fairness and Efficiency in Transaction Ordering
The challenge of fair transaction ordering remains central in any discussion about MEV extraction and auction design. Flashbots’ First Bid Auction – First Come First Served (FBA-FCFS) model offers an innovative compromise: it allows traders to prioritize transactions by bidding (FBA), but ensures that under certain conditions transactions are processed strictly in submission order (FCFS). This approach addresses persistent concerns about front-running and unfair extraction by miners or validators while maintaining high efficiency (source).
The Modular Future: Why Hybrid Settlement Models Matter Now
This convergence of offchain sequencing with onchain guarantees is not just theoretical – it’s reshaping live markets today. For instance:
- Vertex Protocol: Achieves sub-second trade matching via an offchain sequencer while keeping settlements trustless.
- Cero Network: Lets rollups choose their own DA/settlement layers for maximum flexibility.
- CoW Protocol’s batch auctions: Leverage combinatorial batch logic to minimize MEV extraction opportunities during execution (see EthCC talk).
The result? A new era where DeFi protocols can rapidly iterate on their execution stacks without sacrificing security or composability. As more teams adopt these modular approaches, expect further innovations in auction mechanisms, data availability solutions, and even regulatory compliance tooling tailored for hybrid architectures.
What makes hybrid settlement models so compelling is their ability to adapt as DeFi use cases diversify. As protocols mature, the need for transaction speed, composability, and fairness becomes even more pronounced, especially as institutional capital explores on-chain markets and regulatory frameworks begin to take shape. Modular auctions and sequencers provide the scaffolding for this evolution, letting builders combine best-in-class components for their specific needs.
For example, regulated asset markets can leverage hybrid AMM settlement models, like those pioneered by Ohanae, to bridge compliant trading with the efficiency of automated market makers (source). Meanwhile, privacy-centric applications might opt for private DA layers and bespoke settlement paths, choices made possible only through modular architectures.
Risks and Open Questions
Despite the clear benefits, hybrid settlement models are not without challenges. Offchain sequencing introduces new trust assumptions, if sequencers collude or become centralized, censorship or value extraction risks could resurface. Protocols like Cero address this by decentralizing their sequencing networks and allowing rollups to select between shared or dedicated options (source). Still, monitoring these systems for resilience and transparency remains crucial as adoption scales.
Another open question is how these modular systems will interact across chains. As cross-rollup composability becomes a priority, ensuring seamless data availability and settlement across heterogeneous stacks will test even the most advanced architecture designs. The race is now on to develop interoperability standards that preserve both speed and security.
What’s Next? The Road Ahead for Hybrid Settlement in DeFi
The trajectory is clear: hybrid settlement models are becoming foundational to next-generation DeFi infrastructure. By harnessing offchain sequencing for performance alongside modular auctions for flexibility, protocols can address liquidity fragmentation, minimize MEV risks, and unlock new trading strategies previously impossible in monolithic environments.
As highlighted in recent research from Vertex Protocol and Cero Network’s documentation, these innovations are not just academic, they’re driving real improvements in user experience today. Expect further advances in batch auction logic (as seen with CoW Protocol), scalable offchain auction mechanisms (Cryptology ePrint Archive), and new forms of aggregation that blur the line between execution and settlement layers.
Key Trends Shaping Hybrid Settlement Models in DeFi
-

Decentralized Hybrid Sequencers (e.g., Cero Network): Platforms like Cero are pioneering multi-DA, multi-settlement sequencers, enabling rollups to select from shared or dedicated sequencing and multiple data availability layers. This modularity boosts scalability and customizability across DeFi ecosystems.
-
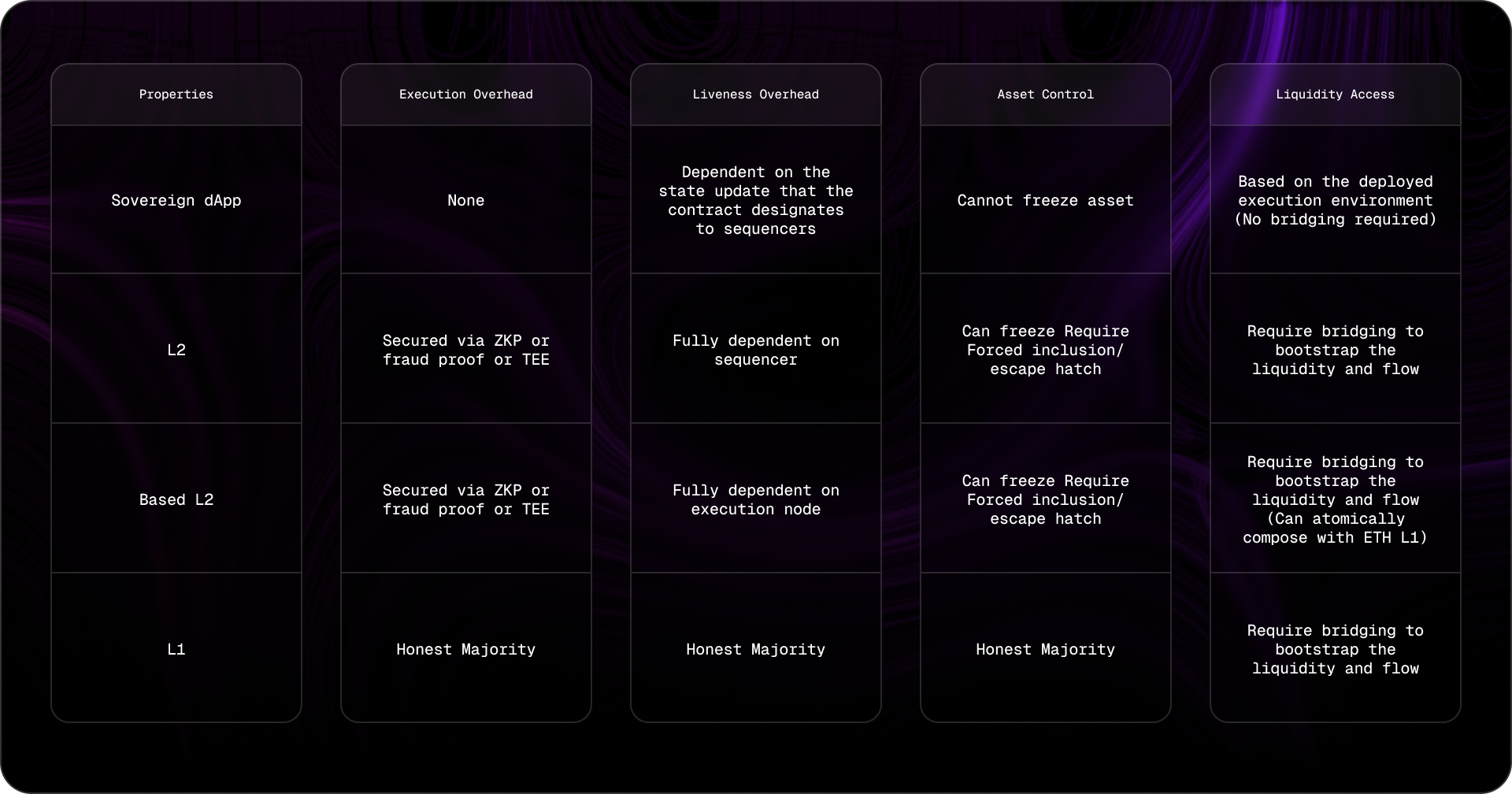
Application-Specific Sequencers (ASS): The rise of application-specific sequencers allows decentralized applications to optimize transaction ordering and settlement for their unique needs, improving both performance and security.
-

Hybrid AMM Settlement for Regulated Markets: Hybrid AMM models, such as those explored by Ohanae, are adapting automated market makers for use in regulated securities markets, bridging DeFi innovation with compliance requirements.
-

Modular Auction Protocols (e.g., Axis Finance): Protocols like Axis Finance are introducing modular auctions, allowing sellers to configure settlement parameters and optimize for fairness, efficiency, and transparency.
-
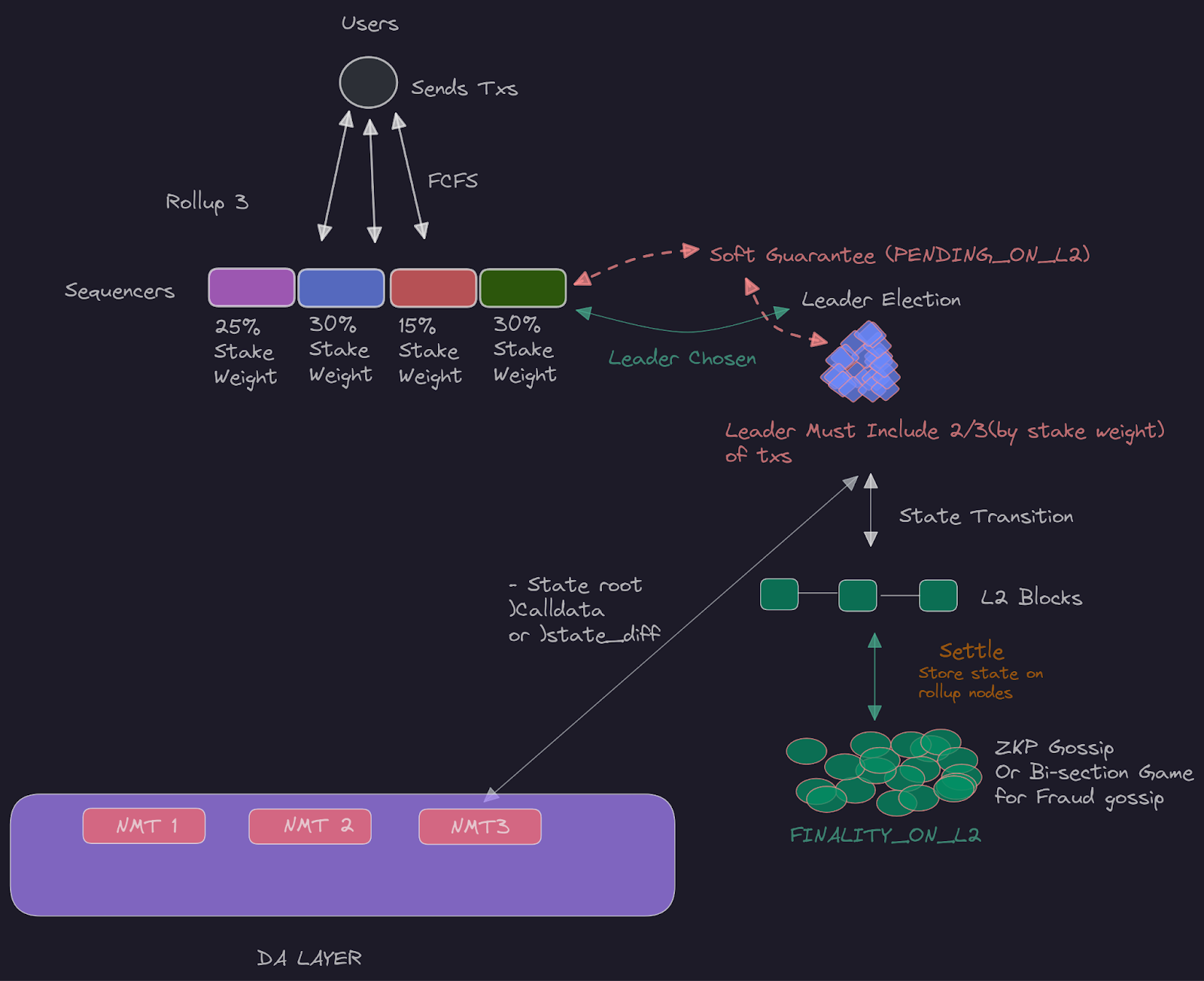
First Bid Auction – First Come, First Served (FBA-FCFS) Models: Flashbots has developed the FBA-FCFS model to address MEV and transaction ordering, balancing fairness with efficient processing in hybrid settlement environments.
-

Off-Chain Sequencing with On-Chain Settlement (e.g., Vertex Protocol): Protocols like Vertex leverage off-chain sequencers for rapid order matching while maintaining on-chain settlement and custody, combining speed with decentralization.
-
Fair Combinatorial Batch Auctions (e.g., CoW Protocol): Innovations like CoW Protocol’s batch auctions are enhancing fairness and efficiency in DeFi execution, reducing the impact of MEV and improving user outcomes.
The coming years will likely see ongoing experimentation as teams push the boundaries of what’s possible with sequencers and modular MEV auctions. For traders, developers, and anyone optimizing transaction flow in DeFi, staying attuned to these shifts will be key to navigating, and thriving in, the next phase of decentralized finance.






